Week 40: LockBit disrupted with 4 arrests; T-Mobile fined $15.75M for breaches; 700K+ DrayTek routers vulnerable; "Joker" malware in Play Store; UK nuclear site fined for cyber lapses
Stay informed with our weekly updates, covering the latest in emerging threats and risks, operational & cybersecurity threats, global regulatory changes, critical vulnerabilities & more.
🔥 Key Highlight
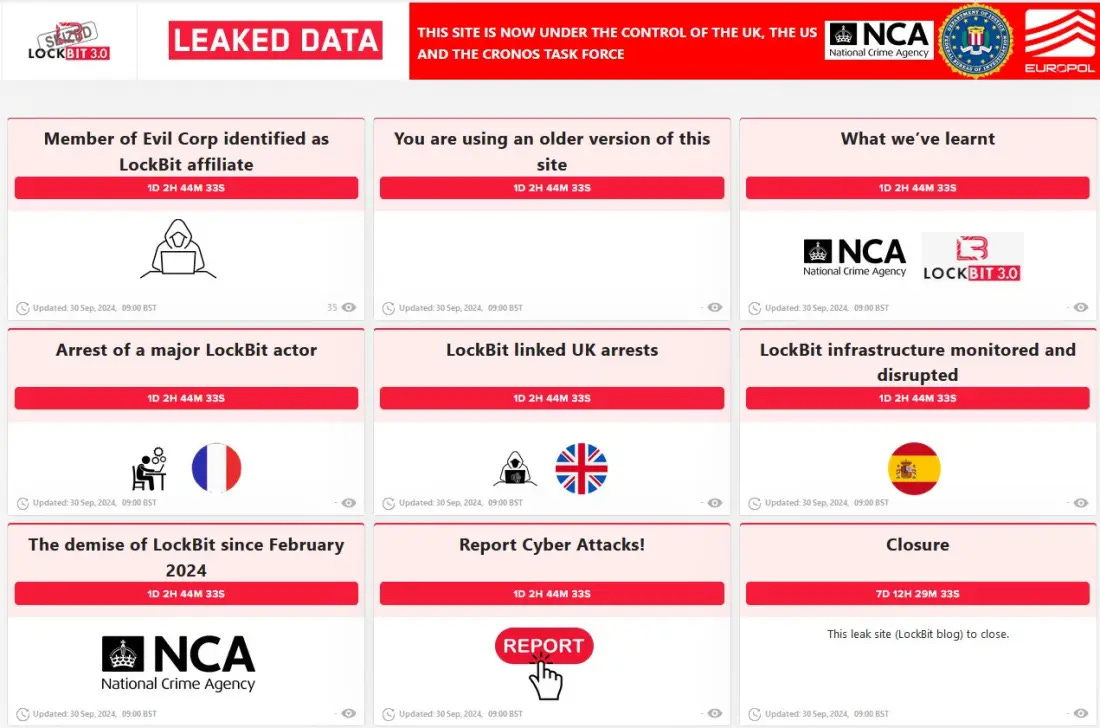
Latest actions against the LockBit ransomware group.
Global Arrests and Sanctions: As part of Operation Cronos, law enforcement from 12 countries, including the US, UK, France, and Australia, executed a coordinated strike against LockBit. Four individuals were arrested:
A suspected developer was arrested in France. Although the provided information does not include his name, this individual's role was crucial in creating or maintaining the ransomware's functionality.
Two affiliates were arrested in the UK for supporting LockBit's activities. Their specific skills or roles within the group weren't detailed, but affiliates often handle the deployment of ransomware, negotiation, or money laundering.
An administrator of a bulletproof hosting service was arrested in Spain. This person's expertise likely involved managing servers that are resistant to law enforcement takedowns, providing a secure platform for LockBit's operations.
Key Figure Identified and Sanctioned:
Aleksandr Ryzhenkov, a Russian national, was sanctioned for his significant role as a LockBit affiliate linked closely with Evil Corp. His skills or exact contributions to LockBit weren't detailed in the excerpts, but his sanctioning indicates he played a pivotal role in financial gains from ransomware activities.
Operational Tactics and Takedown Details:
The takedown involved seizing LockBit's infrastructure, including servers and domains. This was achieved through a combination of technical infiltration, where law enforcement managed to take over LockBit's leak sites and administrative systems, gaining access to source code, victim details, and internal communications.
Crypto tracing and forensic support were utilized to dismantle the financial operations of LockBit, likely involving tracking ransom payments through blockchain analysis.
Disruption Impact:
The actions not only led to arrests but significantly disrupted LockBit's operational capacity. Law enforcement actions revealed the chaotic governance of LockBit, where affiliates operated with little oversight, contributing to its widespread but somewhat disorganized impact.
Background on LockBit:
LockBit operates on a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, where the core group develops the malware and sells access to affiliates, who then conduct the actual ransomware attacks. This model allows for rapid expansion but also introduces variability in operations due to diverse affiliate tactics.
📢Threat Intel & Info Sharing
The U.S. Department of Justice, in collaboration with Microsoft, has seized 107 internet domains linked to Russian state-sponsored hackers known as COLDRIVER. These domains were instrumental in a sophisticated phishing campaign targeting U.S. government officials and NGOs, aiming to steal credentials for espionage.
Taiwanese server manufacturer Quanta has invested in microgrid technology to power its California facilities, purchasing three sets of fuel cell systems for nearly $80 million from Bloom Energy. This move follows an earlier acquisition in April, highlighting the urgent need for reliable energy sources as local utilities struggle to meet the demands of tech-heavy industries like AI datacenters. Quanta's adoption of Bloom Energy's microgrids, which can operate independently of the main grid, showcases a growing trend where tech companies ensure energy independence to maintain competitiveness amidst rising energy demands.
Based on various reports, which remain unconfirmed by official channels, the Israeli military allegedly hacked into the communications system of Beirut's Rafic Hariri International Airport, issuing a warning to an Iranian aircraft not to land. This action reportedly involved threats and resulted in the plane turning back without landing.
Key Group is a ransomware operation targeting primarily Russian users since April 2022. Instead of developing custom malware, they utilize various leaked ransomware builders, including Chaos, Xorist, and others. Their attacks involve phishing emails, multi-stage loaders, and persistence techniques like registry modifications. The group negotiates with victims via Telegram and distributes malware through GitHub. Key Group appears connected to a Russian-speaking group called "huis," known for Telegram spam raids. Their use of publicly available ransomware builders exemplifies a growing trend among cybercriminals. This approach allows relatively unsophisticated actors to conduct ransomware campaigns, potentially leading to an increase in such groups in the future.
💻 Malware and Vulnerabilities
Researchers from ForeScout's Vedere Labs discovered 14 critical vulnerabilities in routers manufactured by DrayTek, with one rated at the maximum severity level. Over 700,000 routers were potentially compromised, predominantly used in commercial settings across Europe, Asia, and beyond. These vulnerabilities could facilitate serious cyber threats including espionage, ransomware, and DoS attacks. DrayTek has since issued patches to apply these fixes.
📰 Breaches, Incidents and Fines
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) settled with T-Mobile over multiple data breaches, imposing a $15.75 million fine and requiring a matching investment in cybersecurity enhancements. This includes adopting zero-trust models and improving multi-factor authentication. The settlement aims to set a precedent for cybersecurity within the telecommunications industry, emphasizing data protection for millions of U.S. consumers affected by the breaches. This follows a pattern of increased regulatory scrutiny on data security across major wireless carriers.
The Community Clinic of Maui, known as Mālama, disclosed that over 123,000 individuals' personal and medical information was compromised in a May cyberattack. This incident, claimed by the LockBit ransomware gang, led to a near two-week closure of the clinic and a significant disruption in services, reverting to manual record-keeping. The breach involved sensitive data like Social Security numbers and financial details. Following the attack, law enforcement and cybersecurity experts were involved, with Europol later making arrests linked to LockBit. Mālama offered affected individuals credit monitoring but not identity theft protection, sparking potential legal action.
Verizon is currently experiencing a network outage affecting major cities like Atlanta, Chicago, and Los Angeles, leaving over 100,000 customers without service. Users are unable to make calls or send texts, with some devices showing "Not Registered on Network" or stuck in SOS Mode. Verizon acknowledges the issue and is working on a fix, but no resolution timeline has been provided.
Sellafield, the UK's largest nuclear site, has been fined £332,500 for significant cybersecurity lapses spanning from 2019 to early 2023. This fine marks the first prosecution under the Nuclear Industries Security Regulations 2003, highlighting failures in IT security practices, despite no evidence of actual harm or hacking incidents. The site, crucial for nuclear decommissioning and waste management, pleaded guilty to neglecting annual security checks, a result partly attributed to industry-wide staffing challenges.
ChoiceDNA, a genetic DNA and facial matching service, accidentally exposed the personal and biometric data of approximately 8,000 individuals due to an unsecured WordPress folder named "Facial Recognition Uploads." This folder, accessible without any authentication, contained sensitive details including facial DNA data, biometric images, and personal information like names and contact details. Cybersecurity researcher Jeremiah Fowler reported the breach, which was promptly addressed by securing the folder.
⚖️ Governments , Policy, Regulations
Federal prosecutors have charged UK national Robert B. Westbrook with orchestrating a "hack-to-trade" scheme, exploiting the Office365 accounts of U.S. company executives to obtain non-public financial reports. By abusing Microsoft's password reset mechanism, Westbrook allegedly accessed sensitive information, enabling him to make millions through insider trading in 2019 and 2020. This case, involving five publicly traded companies, highlights vulnerabilities in email security and the potential for financial gain through unauthorized access to corporate communications. The SEC also filed a civil suit to recover ill-gotten gains, emphasizing the use of advanced technology to combat such sophisticated cyber fraud.
An international law enforcement operation, involving Europol, UK, and US authorities, led to the arrest of four individuals connected to the LockBit ransomware group, including a suspected developer. The operation, part of the ongoing "Operation Cronos," also resulted in the seizure of critical servers and the imposition of sanctions on key figures linked to LockBit and its affiliates. This action continues the global effort to dismantle the LockBit infrastructure, which has been notorious for cyberattacks since 2019, affecting major entities like Bank of America and the UK Royal Mail.
Governor Gavin Newsom of California has enacted legislation compelling automakers to install a feature enabling vehicle owners to disable remote access controls. This law aims to protect individuals, particularly those at risk of domestic abuse, by preventing unauthorized tracking or tampering with the vehicle via remote means. Additionally, the bill prohibits car manufacturers from profiting off this safety feature.
Two former Epsilon executives, Robert Reger and David Lytle, were sentenced to prison for selling consumer data lists to fraudsters, facilitating schemes that defrauded hundreds of thousands, costing tens of millions. Reger received 10 years, Lytle 4 years. Using Epsilon's data, they targeted vulnerable populations, including the elderly, for mail fraud scams. This case, investigated by the U.S. Postal Inspection Service, highlights the severe consequences for those exploiting personal data for fraud, with Epsilon settling separately in 2021 for $150 million. The sentences aim to deter similar crimes, emphasizing protection for the
📑Trends, Reports, Analysis
CERT Polska has identified new instances of the "Joker" malware targeting users through apps available on the Google Play Store, including a beauty camera application with over 100,000 downloads.
Key Points:
App Details:
Name: Beauty Camera
Package: com.onmybeauty.beautycamera
Downloads: > 100,000
Last Update: 17/09/2024
Technical Insights:
The app initiates with a seemingly harmless camera interface but engages in malicious activities through encrypted communication and native code execution.
It decrypts commands from kamisatu.top and dynamically loads a DEX file (Kuwan) from a remote server, which contains the malicious payload.
Malicious Activities:
Subscription Fraud: The malware subscribes users to premium services without consent, using mobile network connections to bypass Wi-Fi and potentially avoid detection.
SMS Interception: It captures and processes SMS messages, likely to steal verification codes or other sensitive information.
Security Measures:
Code Obfuscation: Employs XOR encryption for strings and uses native code to decrypt and execute payloads, complicating analysis.